Conditional Sentence => Conditional Sentences are also known as Conditional Clauses or If Clauses. They are used to express that the action in the main clause (without if) can only take place if a certain condition (in the clause with if) is fulfilled.
Clause => A clause is a group of words that has both a subject and a predicate. Every complete sentence is made up of at least one clause.
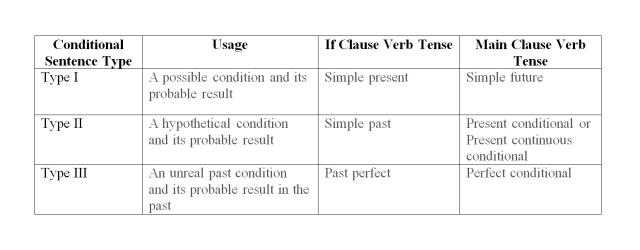
A. Conditional sentence with the word "if"
There are three types:
1. Type I
The sentences are used when it is likely that the condition will be fulfilled
Pattern: if + simple present, will + verb
Example: a. If I have free time, I will go swimming
b. If she invite me, I will come to the party
2. Type II
The sentences are used when it is unlikely that the condition will be fulfilled.
Pattern: if + simple past, would/could/might + verb
Example: a. If it rained tomorrow, I would sleep all day
b. If I had enough money, I would buy a new phone
3. Type III
The sentences are used when it is impossible for condition to be fulfilled because the possibility has already passed.
Pattern: if + past perfect, would/could/might + have + past participle
Example: a. If I had studied, I would have passed the exam
b. If it hadn't rained yesterday, we might have gone sailing
B. Conditional sentence without "if"
1. Type I : Possible to happen in the future
Example: a. Should I have enough money, I will traveling around the world
b. Should you need any help, please call me
2. Type II : Impossible to happen now
Example: a. were I you, I wouldn't get involved
b. Were I rich, I could travel all over the world
3. Type III : Impossible to happen in the past
Example: a. Had I known, I would have said something
b. Had you come home earlier, you could have eaten dinner with us
C. Conditional sentence with the word "wish"
The English word “wish” is used when the speaker wants reality to be different than it actually is. The using 'wish' is to talk about things that are impossible or unlikely.
1. A wish about the present
Example: a. I don't enough time to finish my work, become, I wish I had enough time to finish my work
b. I'm not rich, become, I wish I were rich
2. A wish about the past
Example: a. I didn't wash my clothes yesterday, become, I wish I had washed my clothes yesterday
b. You were not here last night, become, I wish you had been here last night
3. A wish about the future
Example: a. He is not coming with her, become, He wish he were coming with her
b. I don’t like my work, become, I wish I could get a better job.
D. Conditional sentence with the word "hope"
The using hope is mainly expresses a desire that is possible or likely to happen.
1. A hope about the present
Example: a. I hope she is having a wonderful time
b. I hope my mother is on her way now
2. A hope about the past
Example: a. I hope Angelina found her phone
b. I hope he went to the my home yesterday
3. A hope about the future
Example: a. I hope I will find a new boyfriend
b. I hope he can come to my birthday party tomorrow
Sources :